simple_eval_grader
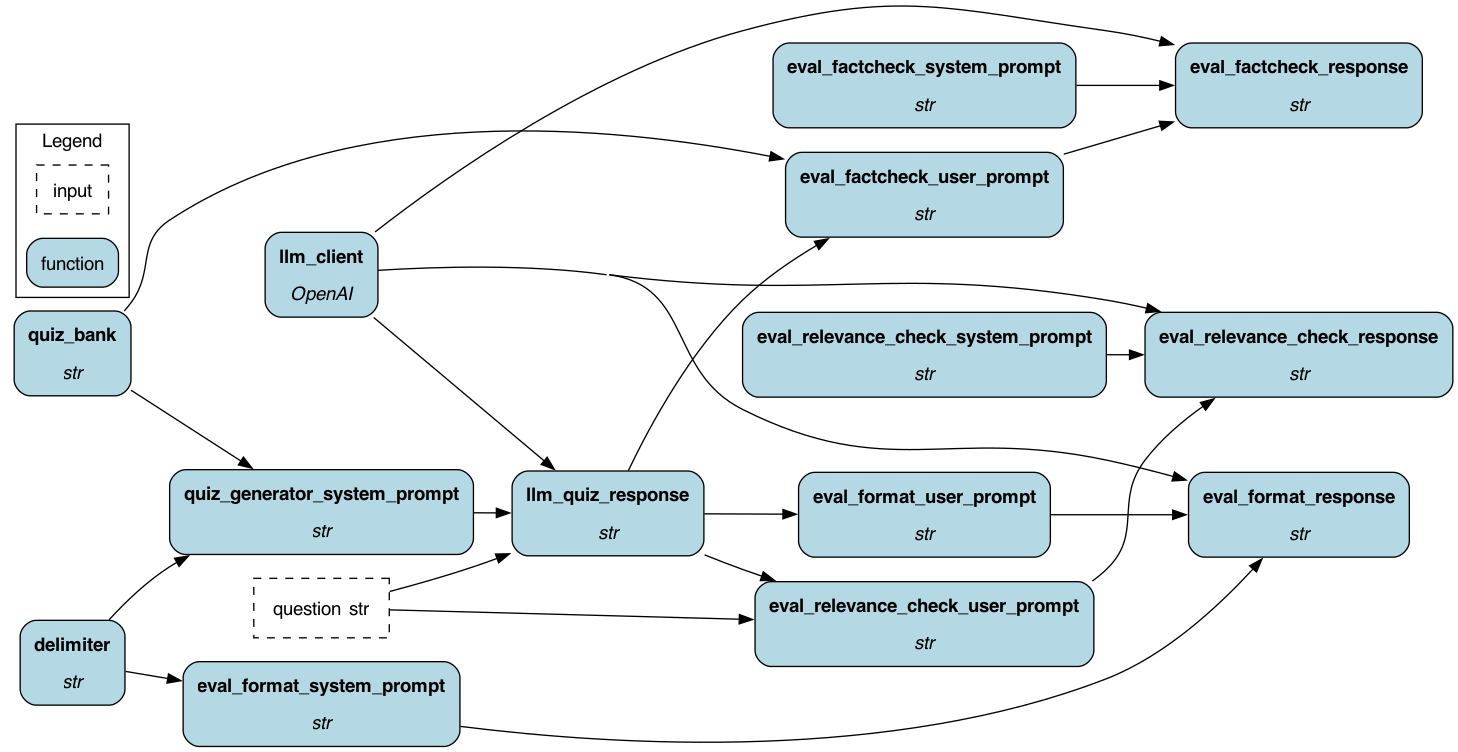
To get started:
Dynamically pull and run
from hamilton import dataflows, driver
# downloads into ~/.hamilton/dataflows and loads the module -- WARNING: ensure you know what code you're importing!
simple_eval_grader = dataflows.import_module("simple_eval_grader")
dr = (
driver.Builder()
.with_config({}) # replace with configuration as appropriate
.with_modules(simple_eval_grader)
.build()
)
# If you have sf-hamilton[visualization] installed, you can see the dataflow graph
# In a notebook this will show an image, else pass in arguments to save to a file
# dr.display_all_functions()
# Execute the dataflow, specifying what you want back. Will return a dictionary.
result = dr.execute(
[simple_eval_grader.CHANGE_ME, ...], # this specifies what you want back
inputs={...} # pass in inputs as appropriate
)
Use published library version
pip install sf-hamilton-contrib --upgrade # make sure you have the latest
from hamilton import dataflows, driver
# Make sure you've done - `pip install sf-hamilton-contrib --upgrade`
from hamilton.contrib.dagworks import simple_eval_grader
dr = (
driver.Builder()
.with_config({}) # replace with configuration as appropriate
.with_modules(simple_eval_grader)
.build()
)
# If you have sf-hamilton[visualization] installed, you can see the dataflow graph
# In a notebook this will show an image, else pass in arguments to save to a file
# dr.display_all_functions()
# Execute the dataflow, specifying what you want back. Will return a dictionary.
result = dr.execute(
[simple_eval_grader.CHANGE_ME, ...], # this specifies what you want back
inputs={...} # pass in inputs as appropriate
)
Modify for your needs
Now if you want to modify the dataflow, you can copy it to a new folder (renaming is possible), and modify it there.
dataflows.copy(simple_eval_grader, "path/to/save/to")
Purpose of this module
This modules shows how to set up LLM based evaluation. The example here is of a quiz app and we want to validate and check the quality of the quiz generated by the LLM. We do this by checking the format, factuality, and relevance of the quiz.
Example Usage
Inputs
These are the defined inputs you can provide.
- question: The user question that specifies what to generate for the quiz
Overrides
With Hamilton you can easily override a function and provide a value for it. For example if you're iterating you might just want to override these two values before modifying the functions:
- quiz_bank: provide a fixed string of context that is the facts for the quiz bank.
- llm_quiz_response: what the LLM returns as the quiz for the user. You can fix this and test the grader functions.
Outputs
You might want to use the following outputs:
- llm_quiz_response: The result of the LLM call to produce the quiz.
- eval_format_response: The result of the format grader.
- eval_factcheck_response: The result of the factcheck grader.
- eval_relevance_check_response: The result of the relevance grader.
Execution
You can ask to get back any result of an intermediate function by providing the function name in the execute call.
Here we just ask for the final result, but if you wanted to, you could ask for outputs of any of the functions, which
you can then introspect or log for debugging/evaluation purposes. Note if you want more platform integrations,
you can add adapters that will do this automatically for you, e.g. like we have the PrintLn adapter here.
## import the module
import pprint
from hamilton import driver
dr = (
driver.Builder()
.with_modules(simple_eval_grader)
.build()
)
dr.display_all_functions("dag.png")
good_response = """
Question 1:##### What is the largest telescope in space called and what material is its mirror made of?
Question 2:##### True or False: Water slows down the speed of light.
Question 3:##### What did Marie and Pierre Curie discover in Paris?
"""
result = dr.execute(["eval_format_response"], overrides={"llm_quiz_response": good_response})
print(result)
assert result["eval_format_response"] == "Y"
bad_response = "There are lots of interesting facts. Tell me more about what you'd like to know"
result = dr.execute(["eval_format_response"], overrides={"llm_quiz_response": bad_response})
print(result)
assert result["eval_format_response"] == "N"
quiz_request = "Write me a quiz about books."
eval_response = dr.execute([
"llm_quiz_response",
"eval_format_response",
"eval_factcheck_response",
], inputs={"question": quiz_request})
pprint.pprint(eval_response)
## Our test asks about a subject not in the context, so the agent should answer N
assert eval_response["eval_format_response"] == "Y"
assert "Decision: Yes" in eval_response["eval_factcheck_response"]
result = dr.execute(
["eval_relevance_check_response"],
inputs={"question": quiz_request},
overrides={
"llm_quiz_response": "Great! Here's a customized quiz about books:\n\n"
"Question 1:#####\n"
"Subject: Leonardo DaVinci\nCategory: Art, Science\n"
"Fact: Leonardo DaVinci is known for his artistic masterpiece, the Mona Lisa. "
"Can you name any other field of study that DaVinci was interested in?\n\n"
"Question 2:#####\nSubject: Paris\nCategory: Art, Geography\nFact: Paris is home to"
" the Louvre, one of the world's largest and most famous museums. Can you name the"
" painting that is displayed in the Louvre and is considered one of the most iconic"
" artworks of all time?\n\n"
"Question 3:#####\nSubject: Starry Night\nCategory: Art\nFact: Vincent van Gogh's "
"painting, Starry Night, is a famous artwork that captures the east-facing view of "
"his room in Saint-Rémy-de-Provence. Can you name any other famous painting by "
"van Gogh?\n\n"
"Feel free to answer the questions and let me know when you're ready for the answers!"}
)
pprint.pprint(result)
How to extend this module
With this example you would likely change all the prompts for your specific use case, since the prompts are specific to the quiz.
Configuration Options
There is no configuration needed for this module.
Limitations
You need to have the OPENAI_API_KEY in your environment.
It should be accessible from your code by doing os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"].
The code does not check the context length, so it may fail if the context passed is too long for the LLM you send it to.
Pytest Integration
Here's an example of how you might use this module with pytest.
from hamilton.contrib.dagworks import simple_eval_grader
from hamilton import driver
import pytest
import pandas as pd
@pytest.fixture
def driver_fixture():
dr = (
driver.Builder()
.with_modules(simple_eval_grader)
.build()
)
return dr
def test_format_grader_works(driver_fixture):
good_response = """
Question 1:##### What is the largest telescope in space called and what material is its mirror made of?
Question 2:##### True or False: Water slows down the speed of light.
Question 3:##### What did Marie and Pierre Curie discover in Paris?
"""
result = driver_fixture.execute(
["eval_format_response"],
overrides={"llm_quiz_response": good_response}
)
assert result["eval_format_response"] == "Y"
bad_response = "There are lots of interesting facts. Tell me more about what you'd like to know"
result = driver_fixture.execute(
["eval_format_response"],
overrides={"llm_quiz_response": bad_response}
)
assert result["eval_format_response"] == "N"
def test_factcheck_grader_works(driver_fixture):
good_response = """
Question 1:##### What is the largest telescope in space called and what material is its mirror made of?
"""
result = driver_fixture.execute(
["eval_factcheck_response"],
overrides={"llm_quiz_response": good_response,
"quiz_bank": "The largest telescope in space is called the Hubble Space Telescope"
" and its mirror is made of glass."}
)
assert "Decision: Yes" in result["eval_factcheck_response"]
@pytest.fixture
def quiz_bank() -> str:
return (
"""1. Subject: Leonardo DaVinci
Categories: Art, Science
Facts:
- Painted the Mona Lisa
- Studied zoology, anatomy, geology, optics
- Designed a flying machine
2. Subject: Paris
Categories: Art, Science
Facts:
- Location of the Louvre, the museum where the Mona Lisa is displayed
- Capital of France
- Most populous city in France
- Where Radium and Polonium were discovered by scientists Marie and Pierre Curie
3. Subject: Telescopes
Category: Science
Facts:
- Device to observe different objects
- The first refracting telescopes were invented in the Netherlands in the 17th Century
- The James Webb space telescope is the largest telescope in space. It uses a gold-berillyum mirror
4. Subject: Starry Night
Category: Art
Facts:
- Painted by Vincent van Gogh in 1889
- Captures the east-facing view of van Gogh's room in Saint-Rémy-de-Provence
5. Subject: Physics
Category: Science
Facts:
- The sun doesn't change color during sunset.
- Water slows the speed of light
- The Eiffel Tower in Paris is taller in the summer than the winter due to expansion of the metal.
""")
test_dataset = [
{"input": "I'm trying to learn about science, can you give me a quiz to test my knowledge",
"expectation": "PASS"},
{"input": "I'm an geography expert, give a quiz to prove it?", "expectation": "FAIL"},
{"input": "Quiz me about Italy", "expectation": "FAIL"},
{"input": "Write me a quiz about books", "expectation": "FAIL"},
]
def test_quiz_creation_with_llm_grader(driver_fixture):
eval_results = []
for test_case in test_dataset:
eval_result = {}
results = driver_fixture.execute([
"llm_quiz_response",
"eval_format_response",
"eval_factcheck_response",
"eval_relevance_check_response",
], inputs={"question": test_case["input"]})
eval_result["input"] = test_case["input"]
eval_result["output"] = results["llm_quiz_response"]
eval_result["format"] = results["eval_format_response"]
eval_result["factuality"] = results["eval_factcheck_response"]
eval_result["relevance"] = results["eval_relevance_check_response"]
eval_result["expectation"] = test_case["expectation"]
if all([results["eval_format_response"] == "Y",
"Decision: Yes" in results["eval_factcheck_response"],
"Decision: Yes" in results["eval_relevance_check_response"]]):
eval_result["actual"] = "PASS"
else:
eval_result["actual"] = "FAIL"
eval_results.append(eval_result)
df = pd.DataFrame(eval_results)
df_html = df.to_html().replace("\\n", "<br>")
print(df_html)
## don't assert anything, just run things and save the results to a dataframe that you
## would probably save/push somewhere.
Source code
__init__.py
import logging
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
from hamilton import contrib
with contrib.catch_import_errors(__name__, __file__, logger):
import openai
def quiz_bank() -> str:
return """1. Subject: Leonardo DaVinci
Categories: Art, Science
Facts:
- Painted the Mona Lisa
- Studied zoology, anatomy, geology, optics
- Designed a flying machine
2. Subject: Paris
Categories: Art, Geography
Facts:
- Location of the Louvre, the museum where the Mona Lisa is displayed
- Capital of France
- Most populous city in France
- Where Radium and Polonium were discovered by scientists Marie and Pierre Curie
3. Subject: Telescopes
Category: Science
Facts:
- Device to observe different objects
- The first refracting telescopes were invented in the Netherlands in the 17th Century
- The James Webb space telescope is the largest telescope in space. It uses a gold-berillyum mirror
4. Subject: Starry Night
Category: Art
Facts:
- Painted by Vincent van Gogh in 1889
- Captures the east-facing view of van Gogh's room in Saint-Rémy-de-Provence
5. Subject: Physics
Category: Science
Facts:
- The sun doesn't change color during sunset.
- Water slows the speed of light
- The Eiffel Tower in Paris is taller in the summer than the winter due to expansion of the metal.
"""
def quiz_generator_system_prompt(delimiter: str, quiz_bank: str) -> str:
return f"""Follow these steps to generate a customized quiz for the user.
The question will be delimited with four hashtags i.e {delimiter}
Step 1:{delimiter} First identify the category user is asking about from the following list:
* Geography
* Science
* Art
Step 2:{delimiter} Determine the subjects to generate questions about. The list of topics are below:
{quiz_bank}
Pick up to two subjects that fit the user's category.
Step 3:{delimiter} Generate a quiz for the user. Based on the selected subjects generate 3 questions for the user using the facts about the subject.
* Include any facts that might be interesting
Use the following format:
Question 1:{delimiter} <question 1>
Question 2:{delimiter} <question 2>
Question 3:{delimiter} <question 3>
"""
def llm_quiz_response(
quiz_generator_system_prompt: str, question: str, llm_client: openai.OpenAI
) -> str:
"""Creates the RAG response from the LLM model for the given prompt.
:param quiz_generator_system_prompt: the prompt to send to the LLM.
:param question: the prompt to send to the LLM.
:param llm_client: the LLM client to use.
:return: the response from the LLM.
"""
response = llm_client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-3.5-turbo",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": quiz_generator_system_prompt},
{"role": "user", "content": question},
],
temperature=0,
)
return response.choices[0].message.content
def delimiter() -> str:
return "####"
def eval_format_system_prompt(delimiter: str) -> str:
return (
"You are an assistant that evaluates whether or not an assistant is producing valid quizzes. "
f"The assistant should be producing output in the format of Question N:{delimiter} <question N>?"
)
def eval_format_user_prompt(llm_quiz_response: str) -> str:
return (
"You are evaluating a generated quiz based on the context that the assistant uses to create the quiz.\n"
"Here is the data:\n"
"[BEGIN DATA]\n"
"************\n"
f"[Response]: {llm_quiz_response}\n"
"************\n"
"[END DATA]\n\n"
"Read the response carefully and determine if it looks like a quiz or test. "
"Do not evaluate if the information is correct only evaluate if the data is "
"in the expected format.\n\n"
"Output Y if the response is a quiz, output N if the response does not look like a quiz."
)
def eval_factcheck_system_prompt() -> str:
return (
"You are an assistant that evaluates how well the quiz assistant "
"creates quizzes for a user by looking at the set of facts available to the assistant.\n"
"Your primary concern is making sure that ONLY facts available are used.\n"
"Helpful quizzes only contain facts in the test set."
)
def eval_factcheck_user_prompt(quiz_bank: str, llm_quiz_response: str) -> str:
return f"""You are evaluating a generated quiz based on the question bank that the assistant uses to create the quiz.
Here is the data:
[BEGIN DATA]
************
[Question Bank]: {quiz_bank}
************
[Quiz]: {llm_quiz_response}
************
[END DATA]
## Examples of quiz questions
Subject: <subject>
Categories: <category1>, <category2>
Facts:
- <fact 1>
- <fact 2>
## Steps to make a decision
Compare the content of the submission with the question bank using the following steps
1. Review the question bank carefully. These are the only facts the quiz can reference
2. Compare the information in the quiz to the question bank.
3. Ignore differences in grammar or punctuation
Remember, the quizzes should only include information from the question bank.
## Additional rules
- Output an explanation of whether the quiz only references information in the context.
- Make the explanation brief only include a summary of your reasoning for the decision.
- Include a clear "Yes" or "No" as the first paragraph.
- Reference facts from the quiz bank if the answer is yes
Separate the decision and the explanation. For example:
************
Decision: <Y>
************
Explanation: <Explanation>
************
"""
def eval_relevance_check_system_prompt() -> str:
return (
"You are an assistant that evaluates how well the quiz assistant "
"creates quizzes for a user by looking at the generated quize questions for relevance to the original ask.\n"
"Your primary concern is making sure that the quiz is relevant to the original user ask.\n"
"Helpful quizzes are what the user asked for."
)
def eval_relevance_check_user_prompt(question: str, llm_quiz_response: str) -> str:
return (
"You are evaluating a generated quiz based on the context that the assistant used to create the quiz.\n"
"Here is the data:\n"
"[BEGIN DATA]\n"
"************\n"
f"[Original Ask]: {question}\n"
"************\n"
f"[Response]: {llm_quiz_response}\n"
"************\n"
"[END DATA]\n\n"
"""## Steps to make a decision
Compare the content of the response with the original ask using the following steps
1. Review the original ask. Every question in the quiz should be relevant to the original ask.
2. Compare the information in the quiz to the original ask.
3. Ignore differences in grammar or punctuation.
Remember, the quizzes should only contain questions that provide what as specified in the original ask.
Read the response carefully and determine if the quiz satisfies to the original ask. "
For example, ask yourself whether each quiz question satisfies the original ask. If any quiz question does "
not satisfy the original ask, output No.
## Additional rules
- Output an explanation of whether the quiz satisfies the original ask.
- Make the explanation brief only include a summary of your reasoning for the decision.
- Include a clear "Yes" or "No" as the first paragraph.
Separate the decision and the explanation. For example:
************
Decision: <Y>
************
Explanation: <Explanation>
************
"""
) # note if you remove the zero-shot CoT like instruction this fails.
def eval_relevance_check_response(
eval_relevance_check_system_prompt: str,
eval_relevance_check_user_prompt: str,
llm_client: openai.OpenAI,
) -> str:
"""Creates the RAG response from the LLM model for the given prompt.
:param eval_relevance_check_system_prompt: the prompt to send to the LLM.
:param eval_relevance_check_user_prompt: the prompt to send to the LLM.
:param llm_client: the LLM client to use.
:return: the response from the LLM.
"""
response = llm_client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-3.5-turbo",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": eval_relevance_check_system_prompt},
{"role": "user", "content": eval_relevance_check_user_prompt},
],
temperature=0,
)
return response.choices[0].message.content
def llm_client() -> openai.OpenAI:
"""The LLM client to use for the RAG model."""
return openai.OpenAI()
def eval_format_response(
eval_format_system_prompt: str, eval_format_user_prompt: str, llm_client: openai.OpenAI
) -> str:
"""Creates the RAG response from the LLM model for the given prompt.
:param eval_format_system_prompt: the prompt to send to the LLM.
:param eval_format_user_prompt: the prompt to send to the LLM.
:param llm_client: the LLM client to use.
:return: the response from the LLM.
"""
response = llm_client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-3.5-turbo",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": eval_format_system_prompt},
{"role": "user", "content": eval_format_user_prompt},
],
temperature=0,
)
return response.choices[0].message.content
def eval_factcheck_response(
eval_factcheck_system_prompt: str, eval_factcheck_user_prompt: str, llm_client: openai.OpenAI
) -> str:
"""Creates the RAG response from the LLM model for the given prompt.
:param eval_factcheck_system_prompt: the prompt to send to the LLM.
:param eval_factcheck_user_prompt: the prompt to send to the LLM.
:param llm_client: the LLM client to use.
:return: the response from the LLM.
"""
response = llm_client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-3.5-turbo",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": eval_factcheck_system_prompt},
{"role": "user", "content": eval_factcheck_user_prompt},
],
temperature=0,
)
return response.choices[0].message.content
if __name__ == "__main__":
import pprint
import __init__ as simple_eval_grader
from hamilton import driver
dr = driver.Builder().with_modules(simple_eval_grader).build()
dr.display_all_functions("dag.png", deduplicate_inputs=True)
good_response = """
Question 1:#### What is the largest telescope in space called and what material is its mirror made of?
Question 2:#### True or False: Water slows down the speed of light.
Question 3:#### What did Marie and Pierre Curie discover in Paris?
"""
result = dr.execute(["eval_format_response"], overrides={"llm_quiz_response": good_response})
print(result)
assert result["eval_format_response"] == "Y"
bad_response = "There are lots of interesting facts. Tell me more about what you'd like to know"
result = dr.execute(["eval_format_response"], overrides={"llm_quiz_response": bad_response})
print(result)
assert result["eval_format_response"] == "N"
quiz_request = "Write me a quiz about books."
eval_response = dr.execute(
[
"llm_quiz_response",
"eval_format_response",
"eval_factcheck_response",
],
inputs={"question": quiz_request},
)
pprint.pprint(eval_response)
# Our test asks about a subject not in the context, so the agent should answer N
assert eval_response["eval_format_response"] == "Y"
assert "Decision: Yes" in eval_response["eval_factcheck_response"]
result = dr.execute(
["eval_relevance_check_response"],
inputs={"question": quiz_request},
overrides={
"llm_quiz_response": "Great! Here's a customized quiz about books:\n\n"
"Question 1:####\n"
"Subject: Leonardo DaVinci\nCategory: Art, Science\n"
"Fact: Leonardo DaVinci is known for his artistic masterpiece, the Mona Lisa. "
"Can you name any other field of study that DaVinci was interested in?\n\n"
"Question 2:####\nSubject: Paris\nCategory: Art, Geography\nFact: Paris is home to"
" the Louvre, one of the world's largest and most famous museums. Can you name the"
" painting that is displayed in the Louvre and is considered one of the most iconic"
" artworks of all time?\n\n"
"Question 3:####\nSubject: Starry Night\nCategory: Art\nFact: Vincent van Gogh's "
"painting, Starry Night, is a famous artwork that captures the east-facing view of "
"his room in Saint-Rémy-de-Provence. Can you name any other famous painting by "
"van Gogh?\n\n"
"Feel free to answer the questions and let me know when you're ready for the answers!"
},
)
pprint.pprint(result)
Requirements
openai