nixtla_statsforecast
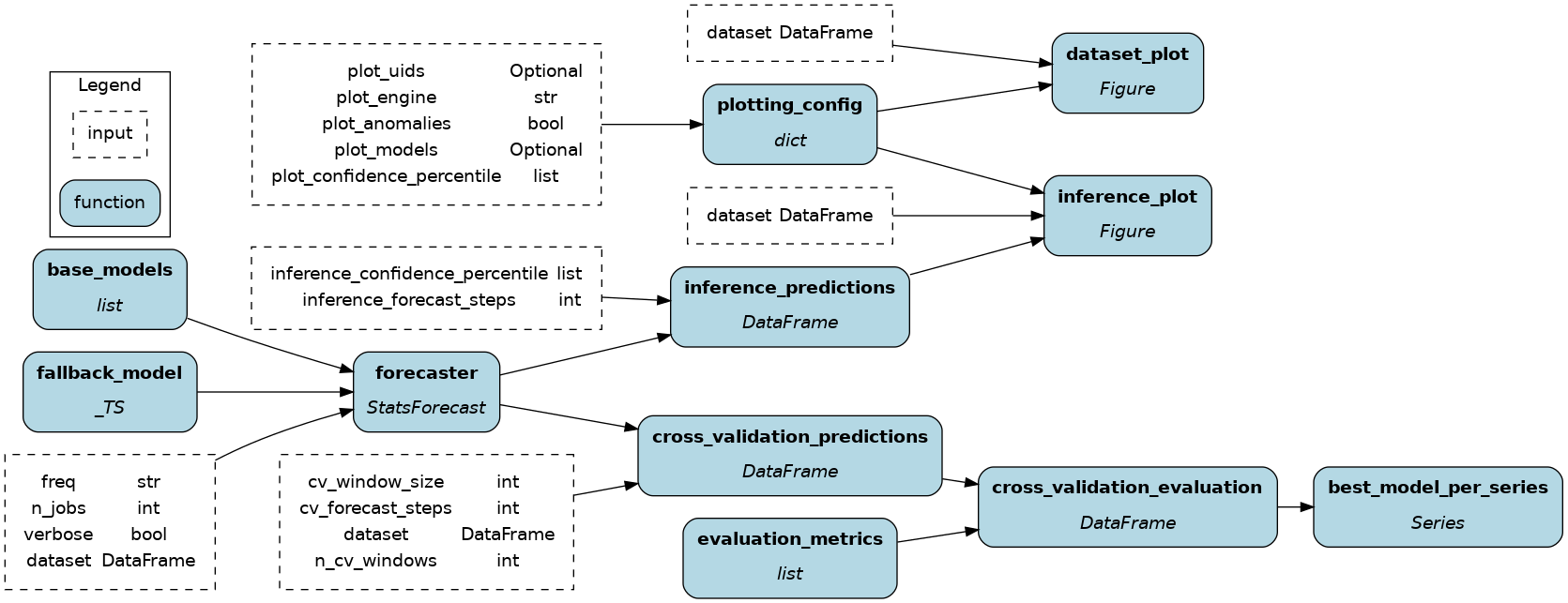
To get started:
Dynamically pull and run
from hamilton import dataflows, driver
# downloads into ~/.hamilton/dataflows and loads the module -- WARNING: ensure you know what code you're importing!
nixtla_statsforecast = dataflows.import_module("nixtla_statsforecast", "zilto")
dr = (
driver.Builder()
.with_config({}) # replace with configuration as appropriate
.with_modules(nixtla_statsforecast)
.build()
)
# If you have sf-hamilton[visualization] installed, you can see the dataflow graph
# In a notebook this will show an image, else pass in arguments to save to a file
# dr.display_all_functions()
# Execute the dataflow, specifying what you want back. Will return a dictionary.
result = dr.execute(
[nixtla_statsforecast.CHANGE_ME, ...], # this specifies what you want back
inputs={...} # pass in inputs as appropriate
)
Use published library version
pip install sf-hamilton-contrib --upgrade # make sure you have the latest
from hamilton import dataflows, driver
# Make sure you've done - `pip install sf-hamilton-contrib --upgrade`
from hamilton.contrib.user.zilto import nixtla_statsforecast
dr = (
driver.Builder()
.with_config({}) # replace with configuration as appropriate
.with_modules(nixtla_statsforecast)
.build()
)
# If you have sf-hamilton[visualization] installed, you can see the dataflow graph
# In a notebook this will show an image, else pass in arguments to save to a file
# dr.display_all_functions()
# Execute the dataflow, specifying what you want back. Will return a dictionary.
result = dr.execute(
[nixtla_statsforecast.CHANGE_ME, ...], # this specifies what you want back
inputs={...} # pass in inputs as appropriate
)
Modify for your needs
Now if you want to modify the dataflow, you can copy it to a new folder (renaming is possible), and modify it there.
dataflows.copy(nixtla_statsforecast, "path/to/save/to")
Purpose of this module
This module implements forecasting using statistical methods with statsforecast by Nixtla.
Fit and evaluate a list of models on a time series dataset. Obtain a cross-validation benchmark dataframe and prediction plots.
Your dataset needs to have columns unique_id to identify each series, ds to identify the time step, and y to specify the value of series unique_id at time ds.
Configuration Options
Config.when
This module doesn't receive configurations.
Inputs
freq: Adjust to meet the sampling rate of your time seriescv_forecast_steps,cv_window_size,n_cv_windows: Change these values to define your cross-validation strategy.- ⚠
n_jobs: Set the number of cores to use for compute. The default value-1will use all available cores and might slowdown the machine in the meantime.
Overrides
base_models: Set the list of Nixtla models to fit and evaluate (docs)evaluation_metrics: Set the list of Nixtla-compatible metrics to use during cross-validation (examples)
Limitations
- This flow doesn't include dataset preprocessing steps.
Source code
__init__.py
import logging
from typing import Callable, Optional
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
from hamilton import contrib
with contrib.catch_import_errors(__name__, __file__, logger):
import matplotlib
import pandas as pd
from statsforecast import StatsForecast
from statsforecast.models import (
_TS,
AutoARIMA,
CrostonClassic,
DynamicOptimizedTheta,
HistoricAverage,
HoltWinters,
SeasonalNaive,
)
from utilsforecast.evaluation import evaluate
from utilsforecast.losses import mse
def base_models() -> list[_TS]:
"""Nixtla stats models to fit and evaluate
Override with your own models at the Hamilton Driver level.
"""
season_length = 24
return [
AutoARIMA(season_length=season_length),
HoltWinters(),
CrostonClassic(),
SeasonalNaive(season_length=season_length),
HistoricAverage(),
DynamicOptimizedTheta(season_length=season_length),
]
def fallback_model() -> _TS:
"""Model to be used if a model fails"""
return SeasonalNaive(season_length=7)
def forecaster(
dataset: pd.DataFrame,
base_models: list[_TS],
fallback_model: _TS,
freq: str = "M",
n_jobs: int = -1,
verbose: bool = False,
) -> StatsForecast:
"""Create the forecasting harness with data and models
:param freq: frequency of the data, see pandas ref: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/timeseries.html#offset-aliases
:param n_jobs: number of cores to use; -1 will use all available cores
"""
return StatsForecast(
df=dataset,
models=base_models,
fallback_model=fallback_model,
freq=freq,
n_jobs=n_jobs,
verbose=verbose,
)
def cross_validation_predictions(
dataset: pd.DataFrame,
forecaster: StatsForecast,
cv_forecast_steps: int = 24,
cv_window_size: int = 24,
n_cv_windows: int = 2,
) -> pd.DataFrame:
"""Fit models and predict over `n_cv_windows` time windows"""
return forecaster.cross_validation(
df=dataset,
h=cv_forecast_steps,
step_size=cv_window_size,
n_windows=n_cv_windows,
)
def evaluation_metrics() -> list[Callable]:
"""List of metrics to use with `utilsforecast.evaluation.evaluate` in `cross_validation_evaluation`
The metric function should receive as arguments at least:
df: pd.DataFrame
models: list[str]
id_col: str = "unique_id"
target_col: str = "y"
See examples: https://github.com/Nixtla/utilsforecast/blob/main/utilsforecast/losses.py
"""
return [mse]
def cross_validation_evaluation(
cross_validation_predictions: pd.DataFrame,
evaluation_metrics: list[Callable],
) -> pd.DataFrame:
"""Evaluate the crossvalidation predictions and aggregate the performances by series"""
df = cross_validation_predictions.reset_index()
models = [m for m in df.columns if m not in ["unique_id", "ds", "cutoff", "y"]]
evals = []
for cutoff in df.cutoff.unique():
eval_ = evaluate(
df=df.loc[df.cutoff == cutoff],
metrics=evaluation_metrics,
models=models,
)
evals.append(eval_)
evaluation_df = pd.concat(evals)
evaluation_df = evaluation_df.groupby("unique_id").mean(numeric_only=True)
return evaluation_df
def best_model_per_series(cross_validation_evaluation: pd.DataFrame) -> pd.Series:
"""Return the best model for each series"""
return cross_validation_evaluation.idxmin(axis=1)
def inference_predictions(
forecaster: StatsForecast,
inference_forecast_steps: int = 12,
inference_confidence_percentile: list[float] = [90.0], # noqa: B006
) -> pd.DataFrame:
"""Infer values using the training harness. Fitted models aren't stored
:param inference_forecast_steps: number of steps in the future to forecast
"""
return forecaster.forecast(
h=inference_forecast_steps,
level=inference_confidence_percentile,
)
def plotting_config(
plot_uids: Optional[list[str]] = None,
plot_models: Optional[list[str]] = None,
plot_anomalies: bool = False,
plot_confidence_percentile: list[float] = [90.0], # noqa: B006
plot_engine: str = "matplotlib",
) -> dict:
"""Configuration for plotting functions"""
return dict(
unique_ids=plot_uids,
models=plot_models,
plot_anomalies=plot_anomalies,
level=plot_confidence_percentile,
engine=plot_engine,
)
def dataset_plot(dataset: pd.DataFrame, plotting_config: dict) -> matplotlib.figure.Figure:
"""Plot series from the dataset"""
return StatsForecast.plot(dataset, **plotting_config)
def inference_plot(
dataset: pd.DataFrame,
inference_predictions: pd.DataFrame,
plotting_config: dict,
) -> matplotlib.figure.Figure:
"""Plot forecast values"""
return StatsForecast.plot(dataset, inference_predictions, **plotting_config)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# run as a script to test Hamilton's execution
import __init__ as nixtla_statsforecast
from hamilton import driver
dr = driver.Driver(
{},
nixtla_statsforecast,
)
# create the DAG image
dr.display_all_functions("dag", {"format": "png", "view": False})
Requirements
matplotlib
numpy
pandas
statsforecast
utilsforecast